Recycling Lives Services: Transforming Waste into Prized Possession Resources
Recycling Lives Services: Transforming Waste into Prized Possession Resources
Blog Article
Discovering Various Types of Waste in Modern Waste Administration Systems
The contemporary landscape of waste administration includes navigating a complex array of waste types, each requiring specialized handling and disposal methods to mitigate ecological effects. Local solid waste, harmful waste, digital waste, and natural waste each present unique obstacles and possibilities for source recovery.
Community Solid Waste
Community strong waste, typically referred to as house garbage or rubbish, incorporates a range of discarded products created by residential, industrial, and institutional resources within a community. This waste stream commonly consists of products such as product packaging, food scraps, lawn trimmings, paper, plastics, fabrics, and thrown out family goods. The monitoring of local strong waste is a vital component of metropolitan planning and public health and wellness, necessitating reliable collection, transport, and disposal systems.
Effective waste management systems are created to minimize environmental effect while taking full advantage of source recovery. Composting organic waste, such as food scraps and yard trimmings, not only minimizes garbage dump usage however additionally produces beneficial soil changes.
Municipalities should likewise address the financial and logistical obstacles associated with waste administration. Applying pay-as-you-throw systems, improving public understanding, and purchasing innovation can substantially improve waste diversion prices. By incorporating these practices, towns can promote lasting communities, decrease greenhouse gas discharges, and conserve natural sources.
Contaminated Materials

Reliable hazardous waste management involves several critical steps: identification, disposal, partition, and therapy. Segregation ensures that dangerous products are stored individually from non-hazardous waste to avoid cross-contamination.
Governing structures, such as the Source Conservation and Healing Act (RCRA) in the United States, provide standards and requirements for contaminated materials administration. Adherence to these policies, coupled with developments in waste treatment modern technologies, is essential in mitigating the threats connected with contaminated materials.
Digital Waste
Electronic waste, generally described as e-waste, represents a swiftly growing difficulty in waste administration systems around the world. This sort of waste includes thrown out electronic devices and tools such as mobile phones, computers, televisions, and various other electronic appliances. The quick speed of technical development, paired with lowering product life-spans and customer demand for the latest gadgets, has greatly raised the volume of e-waste created every year.
E-waste is specifically troublesome because of its intricate composition, usually having harmful compounds like mercury, lead, and cadmium, which pose considerable ecological and health risks if not effectively handled. Conversely, e-waste additionally includes important products such as copper, gold, and silver, which can be recuperated and reused. The double nature of e-waste-- both beneficial and hazardous-- demands specialized handling, reusing, and disposal procedures.
Efficient e-waste management includes stringent regulative frameworks, robust collection systems, and advanced recycling technologies. Public recognition and engagement are critical, as improper disposal practices, such as unlawful discarding and informal recycling, intensify ecological contamination and health and wellness threats. Improving e-waste administration methods is crucial for minimizing eco-friendly influence and recuperating useful sources in an increasingly electronic world.

Organic Waste
Organic waste, comprising kitchen scraps, backyard trimmings, and farming residues, stands for a significant portion of the international waste stream. This kind of waste is biodegradable, suggesting it can be broken down by bacteria into less complex natural compounds. In spite of its potential for all-natural decomposition, inappropriate management of natural waste can cause damaging ecological effects, consisting of the discharge of greenhouse gases such as methane, which add to climate adjustment.
Effective monitoring of natural waste navigate to these guys is critical for lessening these ecological influences (recycling lives services). Composting is an extensively embraced technique, changing organic waste into nutrient-rich compost that can boost dirt health and agricultural performance. In addition, anaerobic digestion is an arising technology that converts organic waste into biogas, a sustainable power source, and digestate, which can be used as fertilizer
Municipalities and waste administration entities should implement robust organic waste collection and treatment programs to optimize the advantages of these processes. Public education campaigns can also play an essential duty in motivating households and businesses to separate natural waste from other sorts of waste. By prioritizing the management of organic waste, societies can reduce landfill usage, lower greenhouse gas discharges, and produce important by-products for agricultural use.
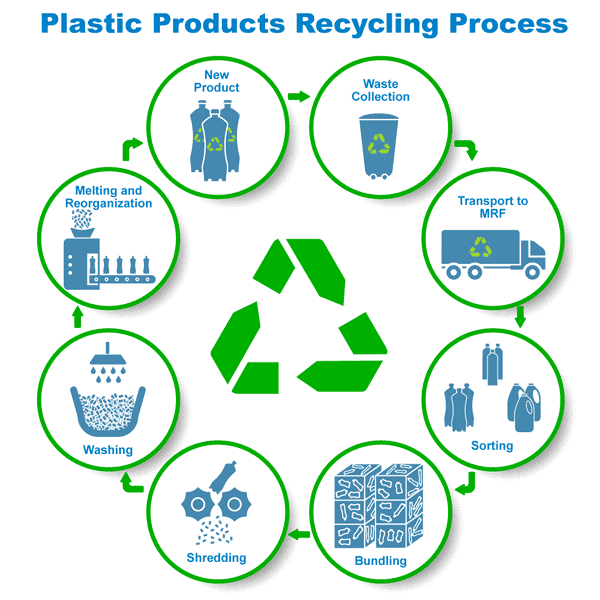
Cutting-edge Waste Monitoring
In the realm of waste management, cutting-edge methodologies are changing exactly how societies handle their refuse, aiming for sustainability and efficiency. One famous development is the implementation of smart waste containers outfitted with sensors that monitor fill degrees and enhance collection routes.
One more significant development is the fostering of waste-to-energy (WtE) modern technologies. By converting non-recyclable waste into usable energy via procedures such as incineration and anaerobic digestion, WtE lowers land fill worry and provides a renewable resource source. Innovations in chemical recycling permit for the break down of intricate plastics right into their initial monomers, allowing the development of brand-new, premium plastic items.
Additionally, the circular economic situation version is obtaining traction, highlighting the layout of products and systems that prioritize reusability and source effectiveness. This all natural method motivates sectors to reduce waste generation from the start. Through these ingenious strategies, contemporary waste management systems are not only addressing the instant obstacles of garbage disposal but likewise leading the way for a much more lasting future.
Verdict
A detailed understanding of metropolitan solid waste, contaminated materials, electronic waste, and organic waste, coupled with the application of cutting-edge waste monitoring services, is crucial for mitigating environmental effects. Integrating innovations such as smart waste bins and waste-to-energy systems can enhance efficiency and sustainability. Efficient waste management strategies not only foster resource recovery but additionally promote public awareness and participation, ultimately adding to the advancement of a circular economic climate.
The modern landscape of waste you could look here monitoring entails browsing an intricate array of waste types, each requiring specialized handling and disposal methods to mitigate ecological influences. Metropolitan solid waste, unsafe waste, digital waste, and natural waste each existing distinctive challenges and possibilities for source recuperation.Digital waste, typically referred to as e-waste, represents blog here a swiftly expanding challenge in waste administration systems globally. Via these cutting-edge approaches, contemporary waste management systems are not only dealing with the immediate challenges of waste disposal yet also leading the way for a much more sustainable future.
A comprehensive understanding of local strong waste, dangerous waste, electronic waste, and organic waste, coupled with the execution of innovative waste administration solutions, is important for mitigating ecological influences. (recycling lives services)
Report this page